Introduction

"Arctic Active Cooling. Endless Possibilities. We capture new technologies in mobile and compact cooling. Full-size cooling in a miniature design, customized to make your device stand out with innovative thermal management."
In the world of modern computing and engineering, cooling systems play a pivotal role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of devices. Among these, the liquid cooled system stands out for its efficiency and effectiveness in heat dissipation. Understanding how these systems work, along with their advantages and disadvantages, is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their setup—be it for gaming or industrial applications.
Understanding Liquid Cooling Systems
A liquid cooling system utilizes a coolant to absorb heat from components like CPUs or GPUs, transferring it away from critical areas to maintain optimal temperatures. This method contrasts sharply with traditional air cooling solutions that rely on fans to circulate air over heatsinks. By exploring what is in a liquid cooling system, we can appreciate the intricate design and technology that allow it to outperform its air-cooled counterparts.
The Basics of Air Cooling
Air cooling relies on airflow generated by fans to dissipate heat from components through metal heatsinks. While generally simpler and more cost-effective than liquid solutions, air cooling can struggle under heavy loads where high-performance hardware generates substantial heat. Evaluating performance and efficiency between these two methods reveals that while air cooling may suffice for everyday tasks, a liquid cooled system often becomes necessary for high-demand scenarios like gaming or intensive computational tasks.
Evaluating Performance and Efficiency
When comparing the performance of liquid versus air cooling systems, several factors come into play including thermal conductivity, noise levels, and overall reliability. Liquid cooled systems typically provide superior thermal management due to their ability to transfer heat more effectively than air alone can achieve. However, understanding both sides—what are the disadvantages of a liquid cooling system?—is key when making an informed decision about which solution best fits your needs.
What is in a Liquid Cooling System?
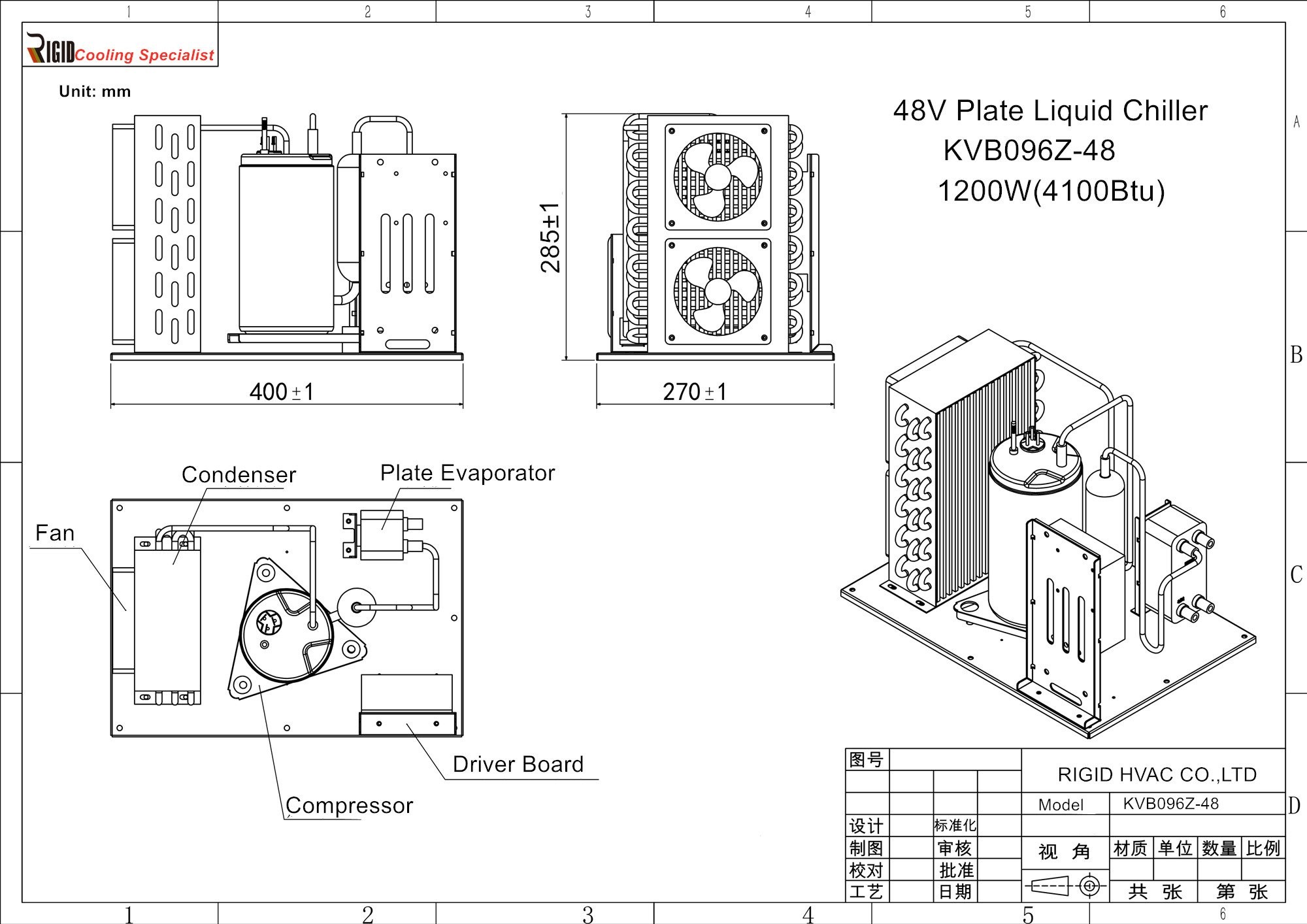
Liquid cooling systems have gained popularity in various applications, particularly in high-performance computing and automotive engines. But what is in a liquid cooling system? This section will delve into the key components, their functionality, and how they stack up against traditional air cooling methods.
Key Components Explained
A liquid cooled system typically comprises several essential components that work together to efficiently manage heat. These include a pump, radiator, water block, reservoir, and tubing. The pump circulates coolant through the system, while the radiator dissipates heat into the environment; the water block absorbs heat from the component it cools—like a CPU or GPU—and the reservoir holds excess coolant to ensure consistent flow.
Understanding these components helps answer questions like Is a liquid cooling system good? for gaming or other high-demand scenarios. Each part plays a critical role in maintaining optimal temperatures and ensuring longevity for your hardware. Moreover, these systems can be customized with various fittings and sizes to meet specific needs.
Functionality and Mechanism
The functionality of a liquid cooling system revolves around its ability to transfer heat away from critical components efficiently. When heated fluid passes through the water block attached to a processor or graphics card, it absorbs excess thermal energy before moving on to the radiator. Once at the radiator, air is blown over it—typically by fans—to cool down the fluid before it's recirculated back into the system.
This mechanism effectively manages temperatures better than traditional air cooling methods because liquids can absorb more heat than air can carry away. Consequently, this leads us to explore one of the main advantages: better thermal performance during intense tasks like gaming or rendering graphics-heavy applications.
Advantages Over Air Cooling
Liquid cooling systems offer several advantages over their air-cooled counterparts that make them appealing for both enthusiasts and professionals alike. First off, they provide superior thermal performance; this means your CPU or GPU can maintain lower temperatures even under heavy load—crucial for gaming sessions where every frame counts!
Additionally, noise levels tend to be lower with liquid cooled systems since they often rely on larger radiators that use slower-spinning fans compared to smaller ones found in air coolers. Of course, there are some disadvantages of a liquid cooling system worth considering as well—such as initial costs and maintenance requirements—but when it comes down to performance efficiency during demanding tasks like gaming or heavy computing workloads, many find that going liquid is worth it.
Is a Liquid Cooling System Good for Gaming?
Thermal Performance in Gaming PCs
One of the standout features of a liquid cooling system is its exceptional thermal performance in gaming scenarios. Unlike air cooling, which can struggle to dissipate heat effectively during intense gaming sessions, water cooling systems manage to keep temperatures significantly lower. This means that your CPU and GPU can maintain peak performance without throttling due to overheating, allowing for smoother gameplay and higher frame rates.
Moreover, what is in a liquid cooling system contributes to its efficiency; typically including components like radiators, pumps, and water blocks that work together seamlessly. These parts ensure that heat is transferred away from critical components more effectively than traditional air coolers can achieve. As a result, gamers who opt for a liquid cooled system often report better overall stability during demanding gameplay.
Noise Levels Compared to Air Cooling
Another advantage of using a liquid cooled system in gaming setups is reduced noise levels compared to air cooling solutions. Air coolers often rely on large fans spinning at high speeds to maintain adequate airflow, which can lead to noticeable noise during intense gaming sessions. In contrast, many water cooling systems utilize quieter pumps and fans that operate at lower RPMs while still providing excellent airflow.
This quieter operation not only enhances the immersive experience but also allows gamers to focus on their gameplay without distractions from loud fan noises. So if you’re wondering what are the disadvantages of a liquid cooling system regarding noise levels—there aren’t many! Most users find that the benefits far outweigh any potential downsides when it comes to sound.
Long-Term Reliability
Long-term reliability is another crucial factor when considering whether a liquid cooled system is suitable for gaming applications. While some may worry about maintenance issues associated with water systems—such as leaks or pump failures—advancements in technology have made modern liquid coolers more reliable than ever before. With proper installation and occasional maintenance checks, these systems can provide consistent performance over time.
Additionally, many manufacturers offer warranties on their products which adds an extra layer of assurance regarding durability and effectiveness over years of use. When comparing this reliability with traditional air coolers—which may degrade in performance due to dust buildup or fan wear—the advantages become clear for serious gamers looking for longevity in their setups.
What are the Disadvantages of a Liquid Cooling System?

While liquid cooling systems have gained popularity for their efficiency and performance, they are not without their drawbacks. Understanding these disadvantages is crucial when considering whether to invest in a liquid cooled system. From costs to maintenance and potential risks, let's dive into what you need to know.
Initial Cost Considerations
One of the most significant barriers to adopting a liquid cooling system is the initial cost. Compared to traditional air cooling solutions, which can be relatively inexpensive, a liquid cooled system often requires a more substantial upfront investment. This includes not only the components themselves but also any additional hardware needed for installation, which can add up quickly.
Moreover, high-quality water cooling kits can be pricey due to advanced materials and engineering involved in their design. If you're on a tight budget or just starting with gaming or computing setups, you might find that air cooling options fit your wallet better while still providing adequate performance. Ultimately, weighing the long-term benefits against this initial cost is essential when deciding if Is a liquid cooling system good? for your needs.
Maintenance and Complexity
Liquid cooling systems tend to be more complex than their air-cooled counterparts, leading to higher maintenance requirements over time. For instance, regular monitoring of coolant levels and potential replacements may be necessary to ensure optimal performance—something that many users may find cumbersome or intimidating. This added complexity can deter those who prefer straightforward plug-and-play solutions.
Additionally, maintaining a liquid cooled system often involves dealing with various components like pumps and radiators that require cleaning and upkeep. If you're not inclined towards tinkering with your setup regularly or lack technical knowledge about What is in a liquid cooling system?, you might want to think twice before making the switch from air cooling systems.
Potential for Leaks
Perhaps one of the most alarming concerns regarding liquid cooling systems is the potential for leaks—a nightmare scenario for any PC builder or gamer! While manufacturers strive for quality assurance in their designs, there’s always an inherent risk that coolant could leak onto sensitive components like motherboards or GPUs, potentially causing catastrophic damage.
This fear of leaks often leads users to wonder about reliability—Is a liquid cooling system good? if it carries such risks? To mitigate this concern, it's crucial to choose reputable brands and products known for quality control; however, even then there's no guarantee against mishaps occurring over time. Ultimately, understanding these pitfalls will help you make an informed decision regarding whether What are the disadvantages of a liquid cooling system? outweigh its benefits.
What is Liquid Cooling System in Engine Applications?

Liquid cooling systems have become an integral part of modern automotive engineering, providing efficient heat management for high-performance vehicles. By utilizing a liquid cooled system, engines can maintain optimal operating temperatures even under strenuous conditions. This technology not only enhances performance but also contributes to the longevity of engine components.
Applications in Automotive Cooling
In automotive applications, liquid cooling systems are employed to regulate engine temperatures and prevent overheating. These systems circulate coolant—typically a mixture of water and antifreeze—through the engine, absorbing heat and dissipating it via a radiator. What is in a liquid cooling system? It includes essential components like water pumps, radiators, hoses, and thermostats that work together to ensure effective thermal management.
The versatility of liquid cooled systems allows them to be used in various types of vehicles—from everyday cars to high-performance race cars. For instance, many sports cars rely on advanced liquid cooling solutions to maximize engine output while maintaining reliability during intense driving conditions. Additionally, electric vehicles often utilize liquid cooling to manage battery temperatures effectively.
Benefits for Engine Performance
One significant advantage of using a liquid cooling system in engines is its ability to maintain consistent operating temperatures across various conditions. This leads to improved efficiency and performance; engines run more effectively when they are neither too hot nor too cold. Furthermore, with better thermal management from a liquid cooled system, manufacturers can design engines with higher compression ratios and turbocharging capabilities without the risk of overheating.
Moreover, the use of water cooling helps reduce noise levels compared to traditional air-cooling methods. The quieter operation can enhance the driving experience significantly for both drivers and passengers alike. Overall, these benefits make it clear: Is a liquid cooling system good? Absolutely—it’s essential for maximizing both performance and comfort.
Comparisons to Traditional Air Coolers
When comparing liquid cooling systems with traditional air coolers in engine applications, several key differences emerge that highlight the advantages of water-based solutions. Air coolers rely heavily on ambient temperature; if it’s hot outside or if airflow is restricted (like during stop-and-go traffic), their effectiveness diminishes significantly. In contrast, a well-designed liquid cooled system maintains steady temperatures regardless of external conditions.
Additionally, what are the disadvantages of a liquid cooling system? While they may require more complex installation processes and maintenance routines than air coolers (due largely to potential leaks), their superior performance often outweighs these drawbacks for most applications. Liquid-cooled systems can handle higher power outputs without compromising reliability or efficiency.
In summary, when considering what is liquid cooling system in engine applications versus traditional air coolers—liquid solutions offer undeniable benefits that enhance overall vehicle performance while ensuring durability over time.
Spotlight on Arctic Active Cooling

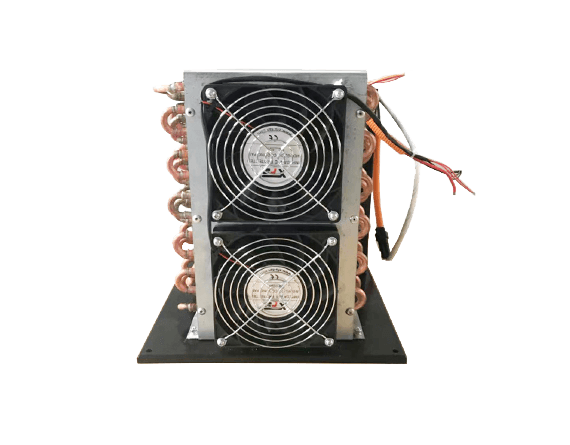
In the realm of cooling solutions, Arctic Active Cooling stands out with its innovative Mini Water Chiller. This liquid cooled system is designed to provide efficient thermal management for various applications, including gaming and industrial machinery. With a focus on compactness and performance, it addresses the essential question: What is in a liquid cooling system? Let's explore its features and how it integrates seamlessly into existing systems.
Features of the Mini Water Chiller
The Mini Water Chiller from Arctic Active Cooling boasts a high-efficient refrigeration mini compressor that utilizes R134a coolant, making it an eco-friendly choice for modern cooling needs. It includes the smallest condenser available, along with a plate evaporator, filter drier, drive board, and other essential refrigeration components—all expertly integrated into one unit. This sophisticated design not only simplifies installation but also ensures that users benefit from cutting-edge micro cooling solutions tailored for diverse applications.
When considering whether a liquid cooling system is good for your setup, the Mini Water Chiller offers significant advantages. Its compact size allows it to fit into tight spaces without compromising performance or efficiency. Additionally, this unit is built with durability in mind—ensuring long-term reliability while keeping noise levels down compared to traditional air coolers.
Integration with Existing Systems
One of the standout features of Arctic Active Cooling's Mini Water Chiller is its ease of integration with existing systems. Customers seeking to enhance their machines or equipment can easily incorporate this liquid cooled system into their designs without extensive modifications. The chiller's control board can connect directly to your bldc compressor driver board, allowing you to adjust compressor speed for optimal performance based on specific operational needs.
This flexibility makes it an attractive option for industries looking to upgrade their cooling capabilities without starting from scratch. Whether you’re upgrading an engine application or enhancing a gaming rig’s thermal management, this water cooling solution provides versatility that meets modern demands.
Benefits for OEM and ODM Projects
For OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) projects, Arctic Active Cooling's Mini Water Chiller presents numerous benefits that can streamline production processes while enhancing product offerings. The ready-to-integrate design means manufacturers can quickly implement this advanced liquid cooled system into their products—saving time and reducing costs associated with custom development.
Moreover, by utilizing state-of-the-art micro and portable commercial refrigeration systems like the Mini Water Chiller, companies can stay ahead in competitive markets where efficiency matters most. As buyers increasingly seek reliable cooling solutions in gaming PCs or automotive applications—understanding what are the disadvantages of a liquid cooling system becomes crucial; however, the advantages offered by this product often outweigh potential drawbacks such as initial costs or maintenance complexity.
In summary, Arctic Active Cooling’s offerings not only address common concerns about what is in a liquid cooling system but also provide practical solutions tailored for varying customer needs across industries.
Conclusion

In the world of cooling systems, the choice between liquid and air cooling is critical for performance and efficiency. A liquid cooled system can offer superior thermal management, especially in high-performance applications like gaming and automotive engines. However, understanding what is in a liquid cooling system, its advantages, and its potential drawbacks is essential for making an informed decision.
Final Thoughts on Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling has emerged as a preferred method for managing heat in various applications due to its efficiency and effectiveness. With components designed to maximize heat dissipation, a liquid cooled system can outperform traditional air cooling setups significantly. However, it's important to weigh these benefits against the complexities involved; after all, what are the disadvantages of a liquid cooling system? Maintenance requirements and potential leaks can deter some users from making the switch.
When to Choose Air Cooling
Air cooling remains a viable option for many users who prioritize simplicity and cost-effectiveness over performance. If you're not pushing your hardware to extremes or if you're working with budget constraints, sticking with air cooling might be your best bet. Additionally, if you find yourself asking Is a liquid cooling system good? but are hesitant about maintenance or leaks, air coolers could provide peace of mind without sacrificing too much performance.
Making the Right Decision for Your Needs
Ultimately, choosing between a liquid cooled system and air cooling comes down to your specific needs and preferences. Consider factors such as your computing workload, noise tolerance levels, and willingness to handle maintenance tasks when deciding which solution is right for you. Whether you're gaming at high settings or looking into what is liquid cooling system in engine applications like automotive technology—understanding both systems will help you make an educated choice that suits your lifestyle.
